KLEE의 기본 명령줄 옵션 개요에서 언급한 대로, KLEE는 심볼릭 환경의 일부로 여러 옵션을 제공한다.
그러나 이러한 옵션의 사용은 새로운 사용자에게는 종종 이해하기 어렵다.
이 튜토리얼은 -sym-arg 및 -sym-files 옵션 중 가장 중요한 것으로 생각되는 옵션에 대한 기본 사용 예제를 제공한다.
-sym-arg 옵션
우리는 -sym-arg <N> 옵션이 테스트 대상 프로그램에 길이 N의 명령줄 인수를 제공한다는 것을 알 수 있다.
이 옵션의 변형인 -sym-args <MIN> <MAX> <N>은 적어도 MIN개의 인수와 최대 MAX개의 심볼릭 인수를 제공하며 각각의 최대 길이가 N을 의미한다.
-sym-arg 옵션을 설명하기 위해 먼저 하드코딩된 비밀번호와 명령줄 인수를 비교하는 다음의 프로그램 소스코드인 password.c를 예로 들겠다.
#include <stdio.h>
int check_password(char *buf) {
if (buf[0] == 'h' && buf[1] == 'e' &&
buf[2] == 'l' && buf[3] == 'l' &&
buf[4] == 'o')
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc < 2)
return 1;
if (check_password(argv[1])) {
printf("Password found!\\n");
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
심볼릭 환경을 활성화하려면, KLEE에 -posix-runtime 옵션을 지정해야 한다.
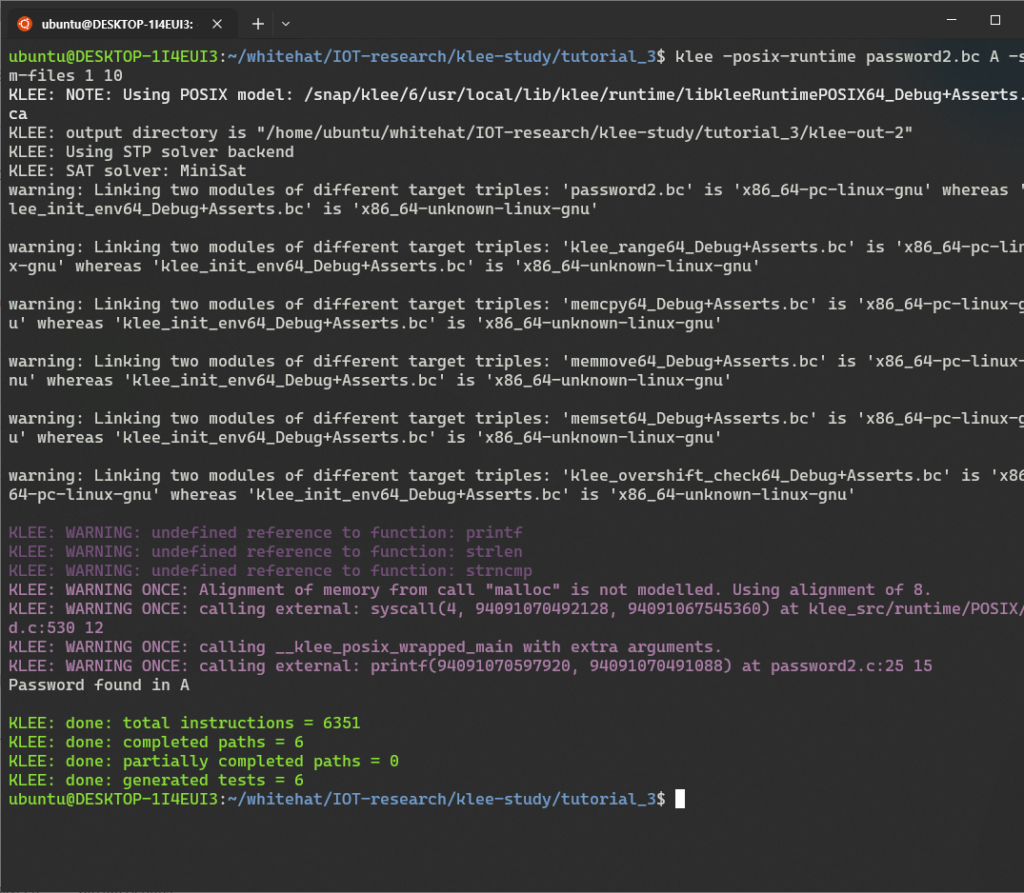
password.c의 bitCode를 입력으로 사용하고, -sym-arg 옵션을 다음과 같이 사용하여 KLEE를 실행한다.
$ clang-11 -emit-llvm -c -g -O0 -Xclang -disable-O0-optnone password.c $ klee -posix-runtime password.bc -sym-arg 5 KLEE: NOTE: Using POSIX model: /snap/klee/6/usr/local/lib/klee/runtime/libkleeRuntimePOSIX64_Debug+Asserts.bca KLEE: output directory is "/home/ubuntu/whitehat/IOT-research/klee-study/tutorial_3/klee-out-0" KLEE: Using STP solver backend KLEE: SAT solver: MiniSat warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'password.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'klee_range64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'memcpy64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'memset64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'klee_overshift_check64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: printf KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: strlen KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: strncmp KLEE: WARNING ONCE: Alignment of memory from call "malloc" is not modelled. Using alignment of 8. KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling external: syscall(4, 93888559554320, 93888557024960) at klee_src/runtime/POSIX/fd.c:530 12 KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling __klee_posix_wrapped_main with extra arguments. KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling external: printf(93888562012160) at password.c:17 5 Password found! KLEE: done: total instructions = 2028 KLEE: done: completed paths = 6 KLEE: done: partially completed paths = 0 KLEE: done: generated tests = 6
보다시피, 명령줄 인수가 심볼릭인 경우, KLEE는 하나의 경로에서 명령줄 인수가 비밀번호와 일치하는 경우를 포함하여 여섯 개의 경로를 실행했다.
-sym-files 옵션
옵션 -sym-files <NUM> <N>는 NUM개의 심볼릭 파일을 생성하며, 첫 번째 파일은 ‘A’로 이름 지어지고 두 번째 파일은 ‘B’로 이름 지어지며 이어서 진행된다.
각 파일의 크기는 N으로 지정할 수 있다.
이 옵션의 유사한 옵션으로 -sym-stdin과 -sym-stdout가 있으며, 각각 표준 입력 및 표준 출력을 심볼릭하게 만든다.
이제 사용자가 지정한 파일에서 문자열을 읽어 하드 코딩된 비밀번호와 일치하는지 확인하는 password2.c 소스코드인 이름의 패스워드 검사기를 고려해보자.
파일 이름이 지정되지 않거나 파일을 열 때 오류가 발생하면 표준 입력에서 문자열을 읽는다.
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int check_password(int fd) {
char buf[5];
if (read(fd, buf, 5) != -1) {
if (buf[0] == 'h' && buf[1] == 'e' &&
buf[2] == 'l' && buf[3] == 'l' &&
buf[4] == 'o')
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int fd;
if (argc >= 2) {
if ((fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) != -1) {
if (check_password(fd)) {
printf("Password found in %s\\n", argv[1]);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
close(fd);
return 1;
}
}
if (check_password(0)) {
printf("Password found in standard input\\n");
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
이제 KLEE를 사용하여 프로그램을 실행한다.
데이터를 읽으려고 시도하다가 프로그램이 멈추는 것을 방지하려면 입력을 제공해야 한다.
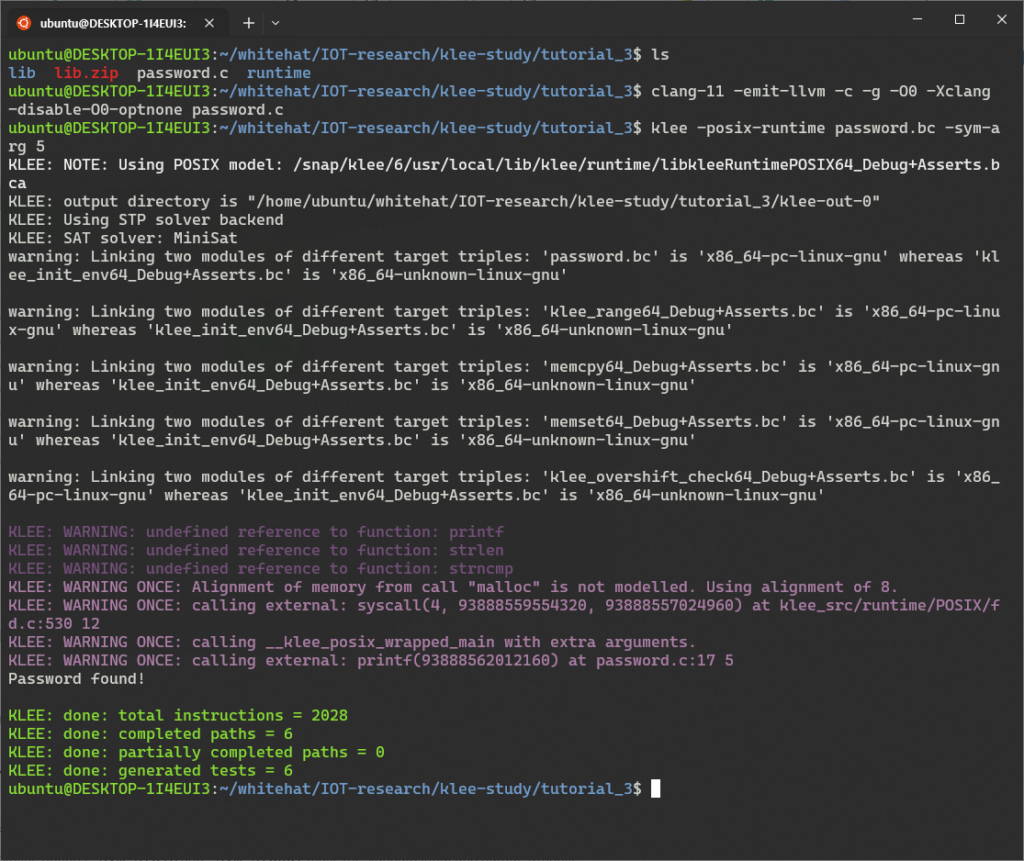
첫 번째 실행에서는 -sym-stdin 옵션을 사용하여 심볼릭 표준 입력을 제공한다.
심볼릭 입력을 제공함으로써 KLEE는 비밀번호 확인이 성공하는 경로를 탐색할 것이다.
$ clang-11 -emit-llvm -c -g -O0 -Xclang -disable-O0-optnone password2.c $ klee -posix-runtime password2.bc -sym-stdin 10 KLEE: NOTE: Using POSIX model: /snap/klee/6/usr/local/lib/klee/runtime/libkleeRuntimePOSIX64_Debug+Asserts.bca KLEE: output directory is "/home/ubuntu/whitehat/IOT-research/klee-study/tutorial_3/klee-out-1" KLEE: Using STP solver backend KLEE: SAT solver: MiniSat warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'password2.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'klee_range64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'memcpy64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'memmove64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'memset64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'klee_overshift_check64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: printf KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: strlen KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: strncmp KLEE: WARNING ONCE: Alignment of memory from call "malloc" is not modelled. Using alignment of 8. KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling external: syscall(4, 94631781707192, 94631778752272) at klee_src/runtime/POSIX/fd.c:530 12 KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling __klee_posix_wrapped_main with extra arguments. KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling external: printf(94631781840032) at password2.c:35 5 Password found in standard input KLEE: done: total instructions = 2934 KLEE: done: completed paths = 6 KLEE: done: partially completed paths = 0 KLEE: done: generated tests = 6
이제 KLEE를 사용하여 비밀번호를 발견해냈다!
우리의 프로그램은 디스크 파일에서 비밀번호를 읽을 수도 있지만, 비밀번호 확인이 성공하는 경로를 실행하도록 KLEE가 파일의 심볼릭 내용을 읽기를 원한다.
-sym-files 옵션은 ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ 등의 이름을 가진 여러 심볼릭 파일을 제공한다.
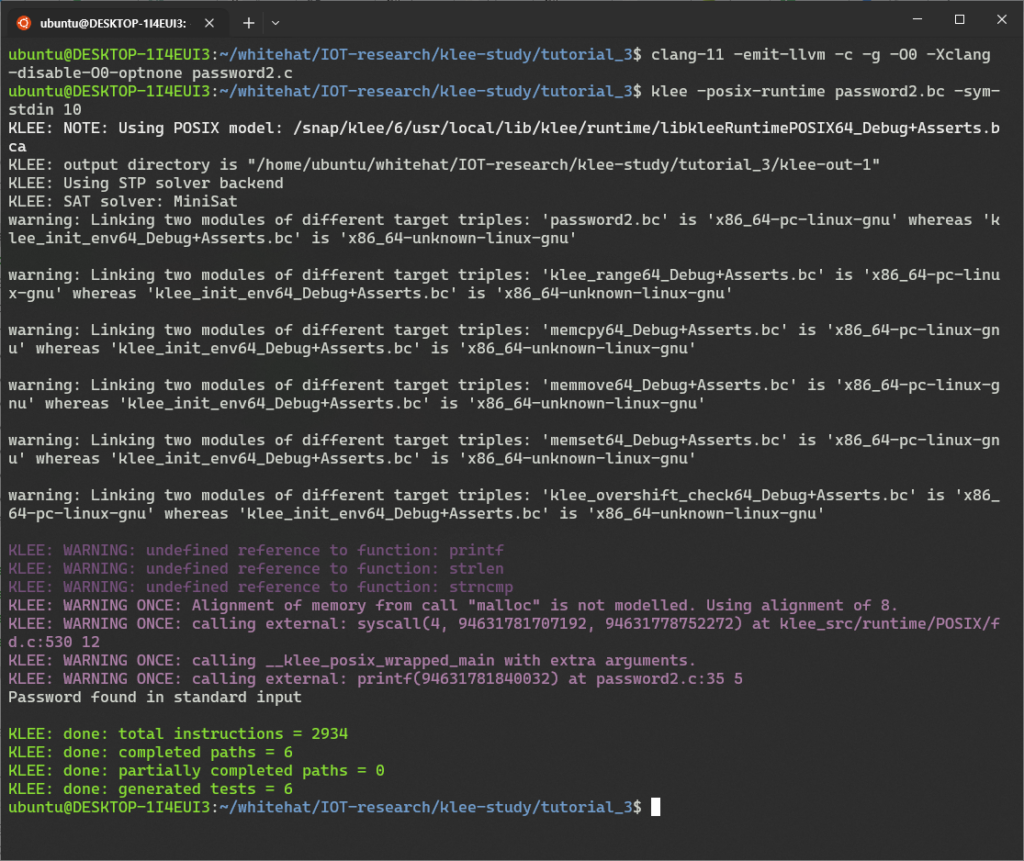
아래의 -sym-files 1 10 옵션을 지정함으로써, KLEE에게 크기가 10바이트인 심볼릭 파일 하나를 제공하도록 요청하고, KLEE는 이 파일을 ‘A’로 이름을 지어준다.
그러므로 이 파일 이름을 우리의 프로그램에 인수로 제공한다.
$ klee -posix-runtime password2.bc A -sym-files 1 10 KLEE: NOTE: Using POSIX model: /snap/klee/6/usr/local/lib/klee/runtime/libkleeRuntimePOSIX64_Debug+Asserts.bca KLEE: output directory is "/home/ubuntu/whitehat/IOT-research/klee-study/tutorial_3/klee-out-2" KLEE: Using STP solver backend KLEE: SAT solver: MiniSat warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'password2.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'klee_range64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'memcpy64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'memmove64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'memset64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' warning: Linking two modules of different target triples: 'klee_overshift_check64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-pc-linux-gnu' whereas 'klee_init_env64_Debug+Asserts.bc' is 'x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu' KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: printf KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: strlen KLEE: WARNING: undefined reference to function: strncmp KLEE: WARNING ONCE: Alignment of memory from call "malloc" is not modelled. Using alignment of 8. KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling external: syscall(4, 94091070492128, 94091067545360) at klee_src/runtime/POSIX/fd.c:530 12 KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling __klee_posix_wrapped_main with extra arguments. KLEE: WARNING ONCE: calling external: printf(94091070597920, 94091070491088) at password2.c:25 15 Password found in A KLEE: done: total instructions = 6351 KLEE: done: completed paths = 6 KLEE: done: partially completed paths = 0 KLEE: done: generated tests = 6
비밀번호는 실행 경로 중 하나에서 심볼릭 파일 A로부터 성공적으로 읽을 수 있었다.